Basic Concepts & Understanding of Communication Systems
Welcome to the very first episode in our Communication System Series! 🎉
Whether you're a curious student or an electronics enthusiast, this blog is your steppingstone to understanding how data travels from one point to another—through invisible waves, wires, or even light!
Let’s build a solid foundation.
🧠 What is a Communication System?
A communication system is a setup that enables the transmission of information (data, voice, video, etc.) from one place (the sender) to another (the receiver). This process can happen through air, cables, or optical fibers—basically, through any transmission medium.
👉 Definition:
A communication system is a set of hardware and software components used to transmit, receive, and process information between two or more entities.
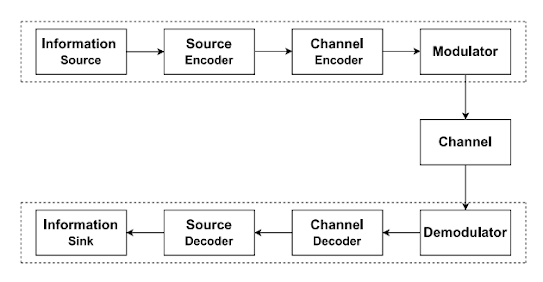
🧩 Basic Block Diagram of a Communication System
Here's a simplified structure of any communication system:
1. Transmitter
The sender or source that generates the message and converts it into a transmittable signal.
➡ Example: A mobile phone microphone capturing your voice.
2. Channel (Transmission Medium)
The pathway the signal travels through. It could be:
Wired (coaxial cable, optical fiber)
Wireless (radio waves, microwaves)
⚠️ Note: This is where noise often interferes and may distort the signal.
3. Receiver
This block extracts the original message from the received signal and converts it back into a human-understandable format.
➡ Example: A speaker playing back your friend's voice during a call.
🌊 Analog vs Digital Communication
Understanding the two types of communication is critical as we move forward in this series.
🔉 Analog Communication
In analog systems, the information is transmitted in a continuous waveform that varies over time.
✅ Pros:
- Better for real-time signals (like voice)
- Simple circuitry
❌ Cons:
- More susceptible to noise
- Harder to store and process
💻 Digital Communication
In digital systems, the information is converted into binary (0s and 1s) and transmitted in discrete packets.
✅ Pros:
- High noise immunity
- Easier to compress, store, and encrypt
- Supports multiplexing (sending multiple signals)
❌ Cons:
- Requires complex processing
- Needs conversion hardware (ADC/DAC)
⚖️ Analog vs Digital: Quick Comparison
🌐 Why Communication Systems Matter
Communication systems are everywhere — from the internet to mobile phones, from satellites to underwater cables. They're the backbone of our digital world.
🧩 Fun Fact: Even your brain is a complex biological communication system using electrical signals through neurons!
🚀 What’s Next in the Series?
In upcoming episodes, we’ll explore:
- Modulation & Demodulation 🔄
- Types of Transmission Media 🌐
- Noise and Signal Distortion ⚠️
- Advanced Concepts like 5G, Li-Fi & IoT 🌟
✍️ Final Thoughts
A solid understanding of the basic communication system sets the stage for diving deeper into electronics, networking, and telecommunications. This foundational knowledge is crucial for students, engineers, and innovators who want to build real-world solutions.
Let’s decode the invisible world of signals, one episode at a time!









Comments
Post a Comment